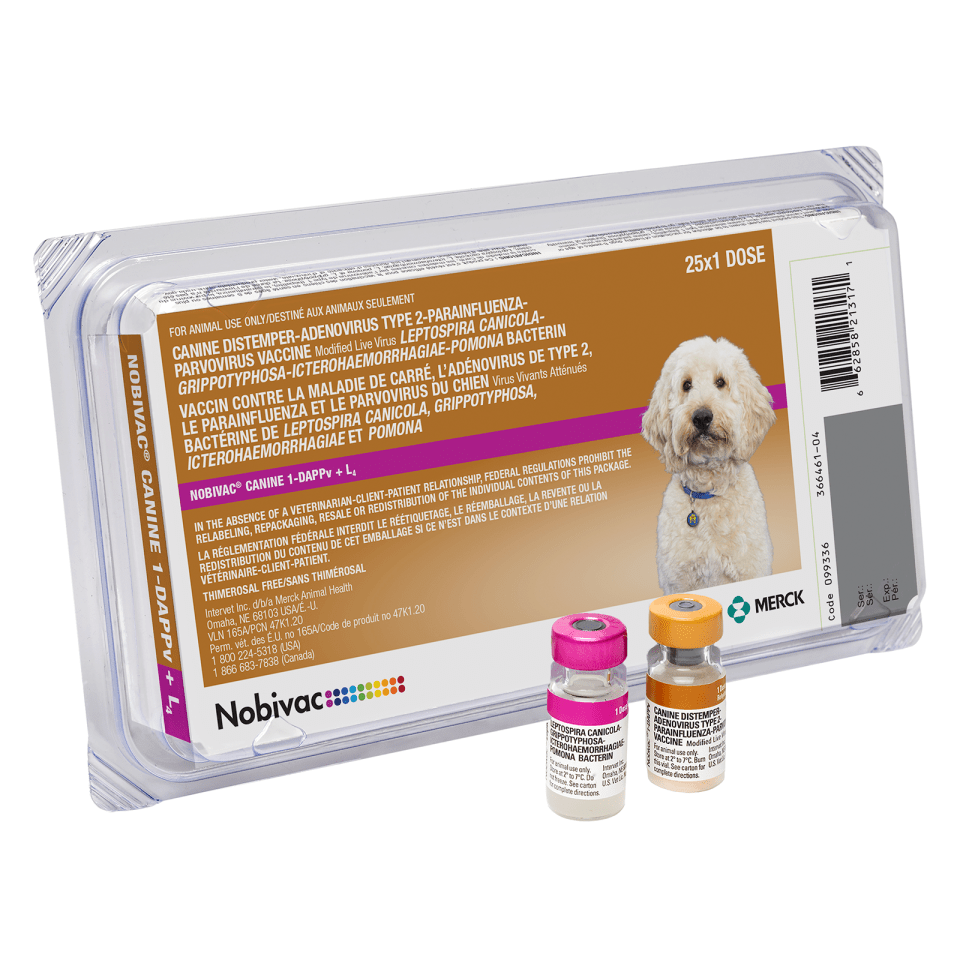
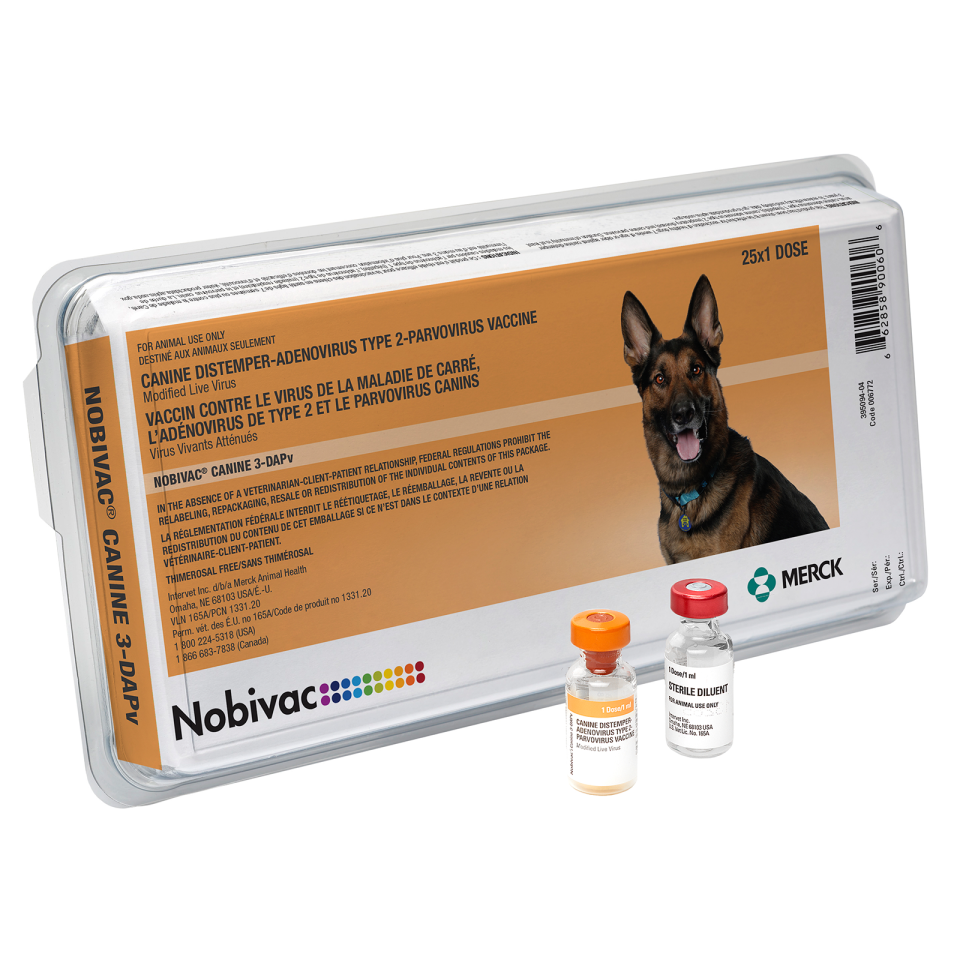
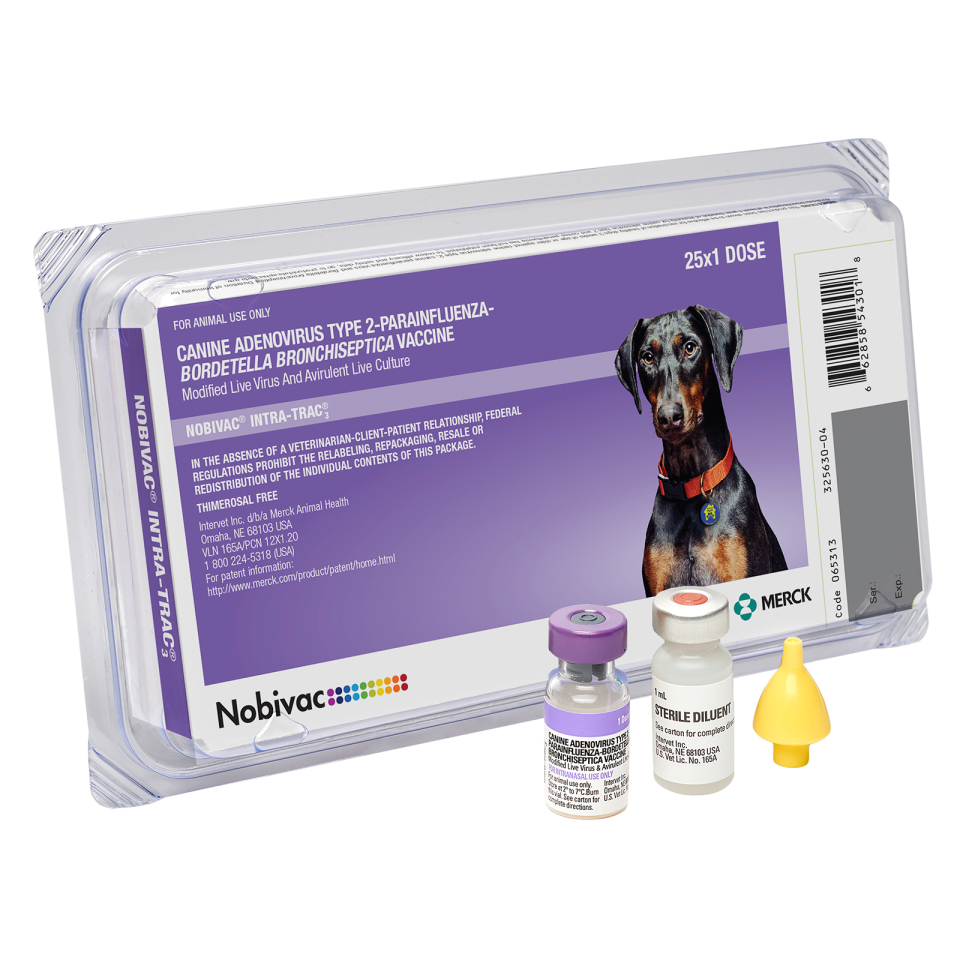
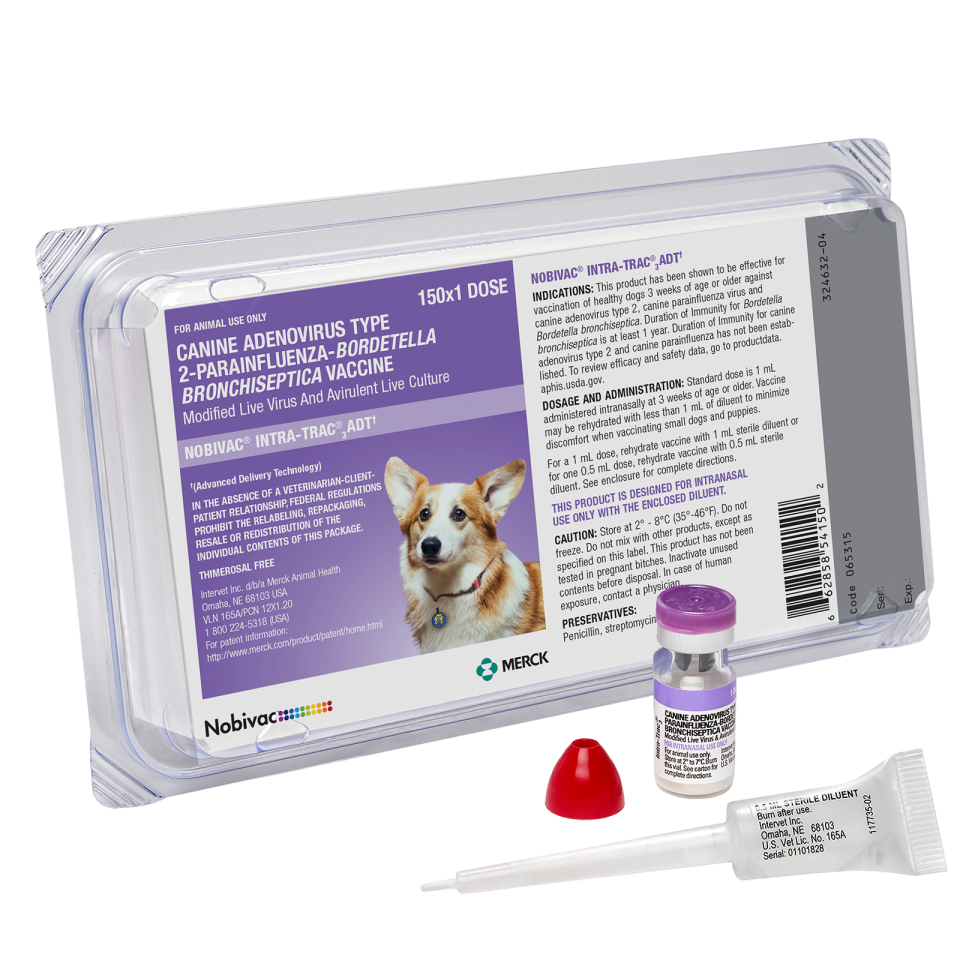
Canine Adenovirus Type 2

Disease Overview
Canine adenovirus type 2 (CAV-2) is related to the hepatitis virus, canine adenovirus type 1 (CAV-1). CAV-2 is used in vaccines to provide protection against canine infectious hepatitis. CAV-2 is also one of the causes of infectious tracheobronchitis, also known as canine cough. 30
Merck Animal Health Solutions
For Canine Adenovirus Type 2
Transmission
Adenoviruses are spread directly from dog to dog through infected respiratory secretions or by contact with contaminated feces or urine.
Clinical Signs30
Respiratory disease (CAV-2)
- Dry, hacking cough (dogs)
- Retching
- Sneezing
- Watery nasal discharge
- Pneumonia, inappetence, fever, and lethargy in severe cases
Hepatitis (CAV-1)
- Fever
- Abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
Risk Factors
- Dogs that come from shelters, rescue centers, breeding kennels, or pet stores
- Boarding at a kennel or doggie daycare
- Visiting groomers, dog parks, or engaging with other dogs on a daily basis
- Dogs that live in multi-pet homes
References:
1. Greene C. Infectious canine hepatitis and canine acidophil cell hepatitis. In: Greene CE, ed. Infectious Diseases of the Dog and Cat. 3rd ed. St. Louis, MO: Saunders/Elsevier; 2006:43.