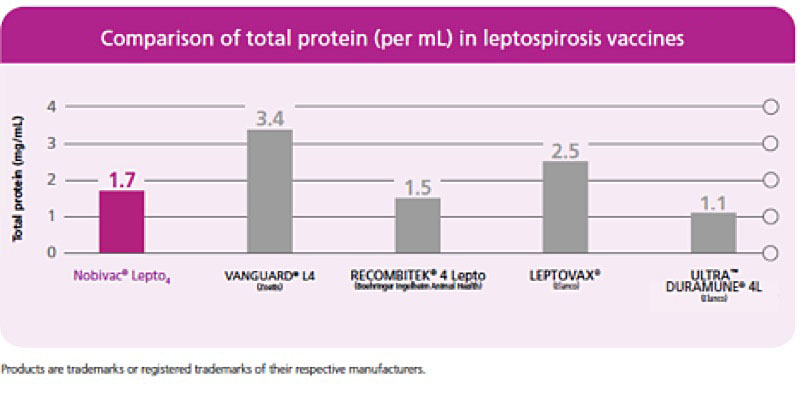
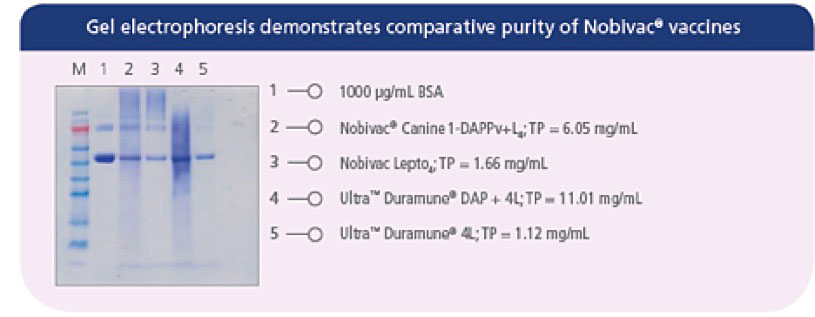
Prevention of Disease and Mortality in Vaccinated Dogs Following Experimental Challenge With Virulent Leptospira.
R LaFleur, J Dant, T Wasmoen. Intervet / Schering Plough Animal Health, Elkhorn, NE.
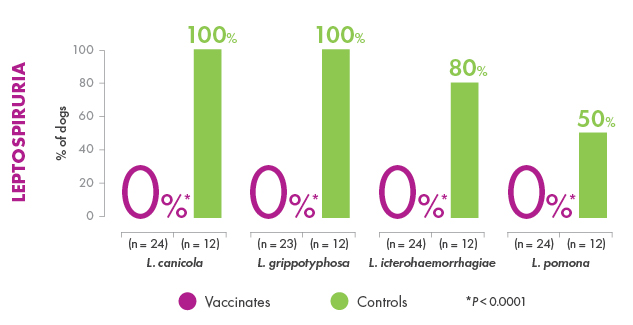
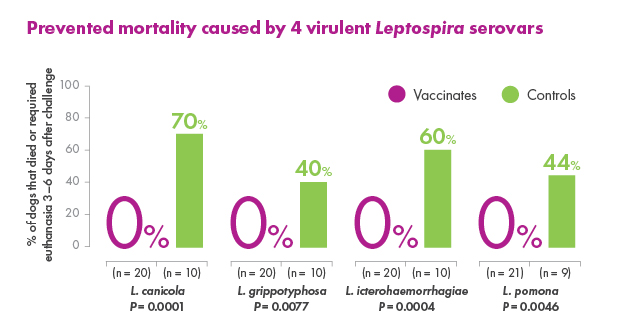
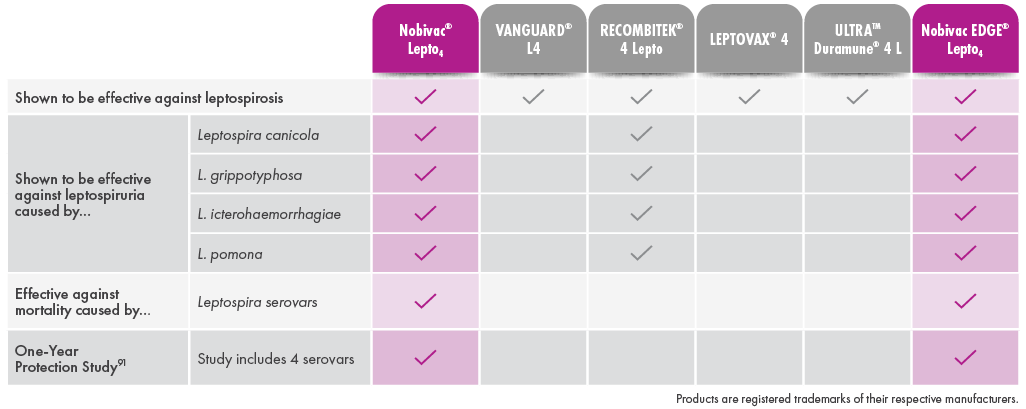
Canine Leptospirosis can vary from subclinical infection to illness that ranges from mild to severe, including death, depending on the susceptibility of the dog, virulence of the organism, and route and degree of infection. The objective of this study was to evaluate the ability of a canine Leptospira bacterin to prevent infection and disease following challenge with virulent Leptospira canicola, L. pomona, L. grippotyphosa, or L. icterohaemorrhagiae. Groups of 8-week-old beagles were vaccinated (day 0) and boosted (day 21) with placebo (n = 10) or the 4-way bacterin (n ≥ 20) and subsequently challenged with each serovar. The results demonstrated that blood and various tissue samples from placebo-recipients became reliably infected, and the dogs developed typical clinical signs of Leptospirosis including loss of appetite, ocular congestion, depression, dehydration, jaundice, hematuria, melena, vomiting, petechiae, and death. In addition, placebo-recipients developed kidney and liver dysfunction. In contrast, some vaccine-recipients became infected, but the organisms were cleared quickly from the blood. Vaccinated dogs failed to develop severe clinical disease requiring medical intervention, and no animals died (p > 0.001). A few of the vaccinated dogs developed clinical abnormalities, but the clinical signs remained mild and were self-limiting (p < 0.0001 for each serovar). Administration of the bacterin also prevented thrombocytopenia (p < 0.0001), kidney complications caused by L. canicola (p < 0.0001), L. icterohaemorrhagiae (p < 0.0001), and L. pomona (p = 0.012), and liver dysfunction caused by L. pomona (p < 0.0001) and L. grippotyphosa (p < 0.0001). The results therefore confirmed that vaccinating dogs with the 4-way Leptospira bacterin provided a high degree of protection (99.5%-100%) against the clinical signs of Leptospirosis including mortality.